In the following the Feynman rules which have been derived in the last section are summarized. To calculate the T-matrix element a Feynman diagram, representing the amplitude to a given order in the perturbation series, can drawn. The Feynman diagram to first order for electron-muon scattering is given by
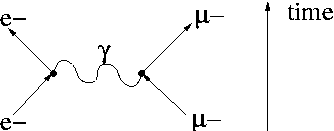

ADDING AMPLITUDES
If several diagrams contribute the corresponding amplitudes have to be added.
For identical fermions these amplitudes have to be subtracted.
SUMMING OVER SPINS
Often, the incoming particle beam is unpolarized, and the polarization of the outgoing particles is not measured. In this case, one has to average over the spins (helicities) of the intial state and to sum over the spins (helicities) of the final state.
In this case, the spin averaged amplitude squared has to be formed when calculating rates or cross sections:



That is, one needs to know trace theorems of the various kinds to evaluate spin averaged amplitudes squared in an analytical way.
To evaluate Feynman diagrams on a computer it is much more convenient to calculate each of the 16 terms indivudually and sum them up.