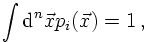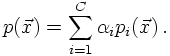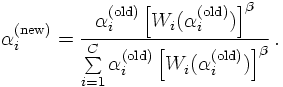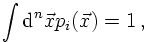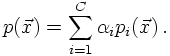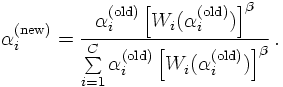Basics
Phase spacing
- One- and two-particle phase space
- Three and more particles
- MC Integration: Sampling
- Smarter sampling methods
MULTI CHANNELING
First of all, C different suitable mappings are defined, each of which with a
p.d.f. according to which the sampling points are distributed. Each of these p.d.f.'s
is normalised to one,
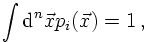 and together with some a-priori weights α they form an overall p.d.f.,
and together with some a-priori weights α they form an overall p.d.f.,
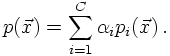 Here, the a-priori weights are also normalised, i.e.
Here, the a-priori weights are also normalised, i.e.
 When a sampling point is to be generated, first of all, the generation channel
has to be specified. This happens through the corresponding α. Thus the
estimator for the integral becomes
When a sampling point is to be generated, first of all, the generation channel
has to be specified. This happens through the corresponding α. Thus the
estimator for the integral becomes
 The variance in each channel is given by some parameter W
The variance in each channel is given by some parameter W
 leading to an overall error defined by
leading to an overall error defined by
 This clearly signlas that the name of the game here is to choose the 6alpha; such that
W(α) gets minimal. This is done iteratively, by rescaling the α in each
iteration step according to
This clearly signlas that the name of the game here is to choose the 6alpha; such that
W(α) gets minimal. This is done iteratively, by rescaling the α in each
iteration step according to
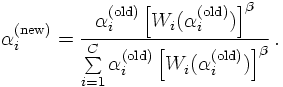 Here, β is a free parameter steering the convergence/damping behaviour of
rescaling the α, it is usually chosen at values between ¼ and ½.
Here, β is a free parameter steering the convergence/damping behaviour of
rescaling the α, it is usually chosen at values between ¼ and ½.
- Selection according to a distribution: Unweighting
- Unweighting: Hit-or-miss
- Problems